There were several articles in 2019 attempting to address the Russian anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) problem set, in my view an unfortunate term that got transported from the China watcher community and slapped onto Russia, even though it has preciously little application in Russian military strategy or doctrinal thought. In a late 2019 WOTR article, which proved quite long, I sought to tackle the operational level thinking in the Russian military for how different capabilities listed under the A2/AD umbrella are likely to be used, illustrating that no A2/AD defensive doctrine or strategy exists. Russian forces are organized around offensive/defensive strategic operations which do not suggest the intention to sit back in a defensive bubble and get eaten by a U.S. led aerosopace attack.
However, this post is about the tactical side of things, and a series of claims made by colleagues about Russian A2/AD capabilities being overrated that I think need addressing. Technology fetishism and threat inflationism seems to be giving way to a dismissive attitude in some circles which is equally problematic. In my view these capabilities are misunderstood. I will briefly tackle air defense and a couple items I think it’s useful to consider on this subject. Just to be frank, this is going to be fairly rudimentary because I’m not an engineer and math is not my preferred language – on the other hand readership dramatically declines with each math formula or table you include in a post.
The first challenge with Russian air defense is the almost wanton confusion between Aerospace Forces (VKS) fielded systems, ground forces fielded air defense systems (PVO-SV), and the Russian air force within the VKS, which is often missing from this picture. Basically, much of the writing presumes that Western forces can fight the S-400 on its own, and you have a number of reports from well meaning countries that attempt to simulate the battle of NATO versus Kaliningrad, as though Kaliningrad was a country and not a tiny grouping of Russian forces relative to the whole. Given Russian framing of any conflict with a coalition of states as a regional war, we need to think about how Russian forces organize for large-scale warfare in the TVD (theater of military operations), and in a geographical span running roughly from Norway to Turkey rather than some contrived pinky fight in the Baltics.
IADS belonging to VKS
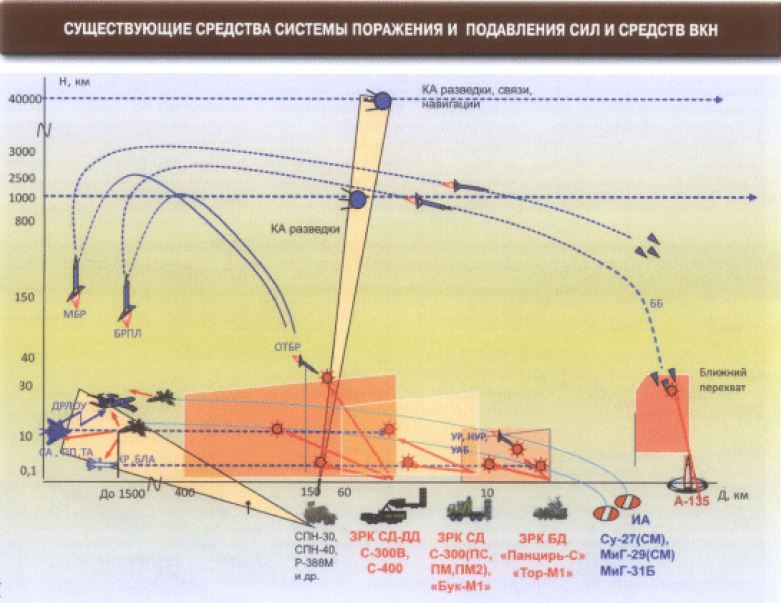
Integrated air defense systems under VKS include the S-300 line of S-300PMU1/2, S-400, S-350 and point defense systems like Pantsir-S1. These systems are used to defend Russian critical infrastructure and ‘strategic deterrent forces’ assigned to execute strategic operations. They may cover Russian ground forces, but are not necessarily vested in defending them since the army has its own air defense component. While the S-400 may be ‘overrated,’ the echelonment of these systems creates layers of defenses at different ranges, but most importantly with different types of missile seekers. These systems provide overlapping coverage for maximum attrition, but what they really do is defend critical civilian and military objects at operational or strategic depths.
The 200km 48N6E2 and the 250km 48N6E3 is semi-active, but the much shorter range 9M96 series (60-120km) is active radar homing. The extended range 40N6 400km missile appears to have achieved initial operating capability, and also comes with an active radar seeker, although I’ve never seen the container for it. These systems excel at medium-high altitude, while the active radar homing missiles pose a challenge for pop-up attacks, low-flying aircraft, or helicopters. We will touch on low altitude penetration a bit later.
Although there have been claims that you can simply take out one engagement radar and thereby neutralize an entire battery of 6-8 TELs, it’s not clear that this is remotely true. That would somewhat defy the concept of integrated air defense and it’s probably not quite that simple given the proliferation of automated systems of command and control at all echelons of the Russian armed forces. It would be safer to assume the Russian VKS thought of that and there’s a Plan B + Plan C to ensure redundancy. This assumes that TEL #1 can only talk to fire control radar A, but cannot communicate with fire control radar B assigned to TEL #9, even though there are dedicated C3 vehicles deployed with them to enable high bandwidth communication.
Typically these systems are co-located with Pantsir-S1 batteries which provide defense against cruise missiles, and missiles intended to take out the S-400. There will also be plenty of EW systems to make life more complicated and effect disorganization on the incoming aerospace strike.
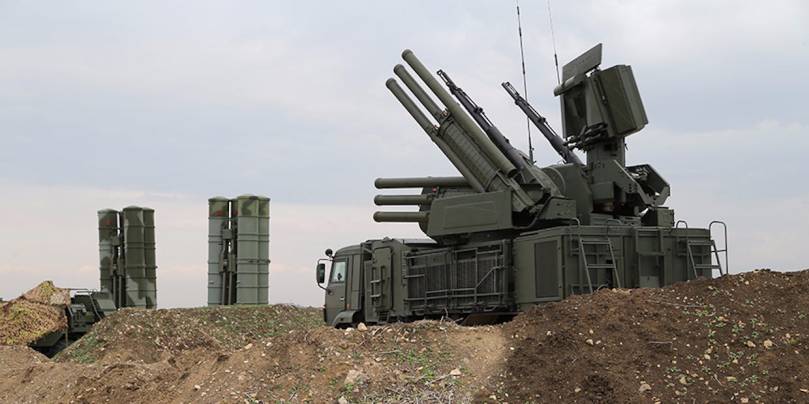

The main problem for Russian air defense is stealth and saturation. The former can offer considerable standoff relative to the effective engagement range, and the latter can simply overwhelm with munitions, decoys and drones. Low observation characteristics substantially reduce the effective range of fire control radars, which means that most of the range rings shown as ‘angry circles of death’ are meaningless. This is part of the reason why there is no Russian strategy based around bubble defense, because it’s not really possible against 5th gen, and even less so against cruise missiles. Hence there is no area denial, and not necessarily anti-access either – think more attrition, disorganization, and deflection.
However, statements about the advantage of low observation aircraft should come with caveats. Stealth does not mean invulnerability. The proliferation of increasingly mobile low-frequency Russian radars, like Nebo-M, which operate in the L-band, VHF, and UHF, means that stealth aircraft can be seen, just not necessarily engaged. These radar systems used to be quite large and clunky due to the antenna aperture required, but are now far more portable with shorter setup times. That said, any air defense network starts to develop gaps once you take down enough radars.
Most of the arguments about a Russian A2/AD strategy based on zonal defense amount to defense intellectual gobbledygook attempting to portray Russia as 1973 Egypt (limited offense followed by area defense). Here is a good example of how Russian writing depicts the problem of deflecting and attriting an aerospace attack. Note the emphasis is on the stack of threats in the aerospace domain, from low-altitude to space based assets, and the ability of Russian air defense to defense critical infrastructure/strategic deterrent forces.
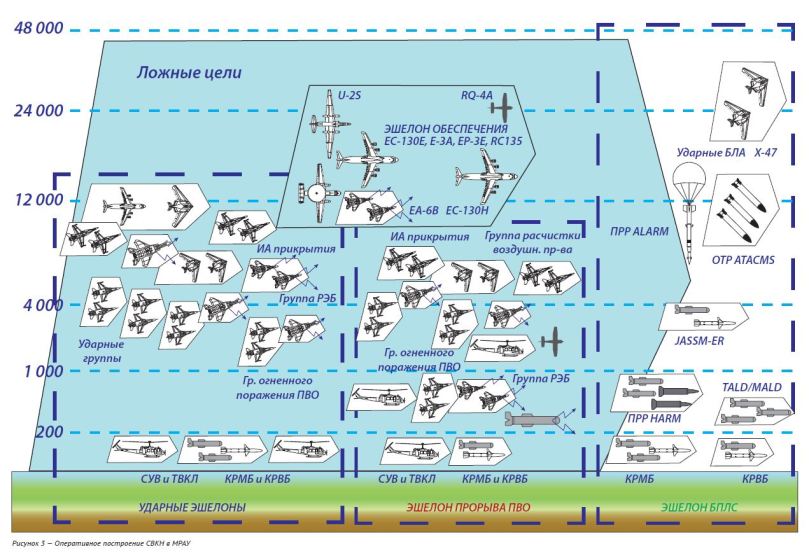
Reading Russian military thought articles on the problem of U.S. massed aerospace assault, and the damage that numerous long range precision guided munitions could inflict, one gets the impression that they understand where things stand perfectly well – and they don’t like it.
That leads us to the second problem, the air force component of the Aerospace Forces, which is probably somewhere in the range of ~800 tactical aircraft. The majority of these have been modernized or replaced with new variants 2011-2019. These fighters are an integral part of the Russian air defense network, and will be looking to engage any aircraft penetrating it, which will be seen on low frequency search radars whether they are 5th gen or 4th gen.
A fair bit of writing presumes that one can perform a SEAD or DEAD mission, tackling VKS owned IADS separately, while the entire Russian air force sits parked and waits for its turn to fight, which is unlikely. Russian fighters will naturally fill the corridors or gaps between Russian air defenses, and will be guided by radar systems that can see low observation aircraft. The Su-57 seems well suited for that role. The limited availability of AWACS aircraft (A-50U) in the Russian air force is an enduring issue, but Russian fighters are primarily guided to intercept via ground control stations utilizing ground based radar. The air defense system as a strategic network is really a combination of radars, integrated air defense, tactical aviation, and missile defense.
Here is a list of aircraft deliveries I pulled from BMPD’s recent update.
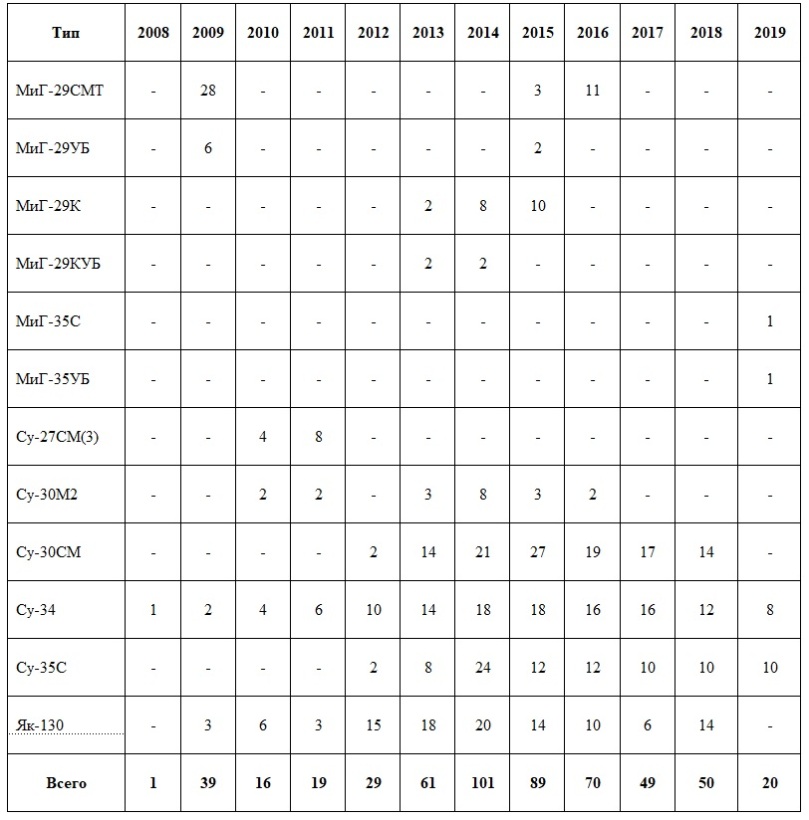
My sense is that the 5th gen versus modern IADS + air force is the sort of thing that will either go really well, or quite poorly, without a lot of in between. Either way the Russian air force is likely to preemptively conduct its own aerospace assault, as part of the strategic aerospace operation, and together with long range aviation wipe out as many air assets as possible on the ground (covered in the WOTR article). Cruise missiles don’t really care if you have 4th gen or 5th gen on the runway. Remove air refueling and AWACS from the picture, things start to get less rosy.
What about Low-Altitude?
It has been asserted that one could simply negate the range of many of these systems with low altitude penetration, going in old school to negate the advantage of long range radar air defense systems. One can understand the visual appeal, complete with Kenny Loggins’ Danger Zone playing in the background. There are a few problems with this theory. The first is that 5th gen aircraft are optimized for the medium-high altitude penetration mission – stealth loses a lot of its value if you can literally see the plane and shoot it down with almost any type of short range system (SACLOS/IR/SPAAG/bow and arrow).
It’s not clear to what extent any Western air force, with the exception of Israel, spends much time training for low-altitude penetration, and while the aircraft can do it, many pilots probably cannot. Without training, nap-of-the-earth flight is likely to result in disaster before Russian air defense can even have a chance to shoot something down.
The second problem is that it’s not a cure-all given many Russian radars are found raised on masts, plus most Russian systems carry a shorter range active radar seeking missile variant. As the S-350 proliferates in the VKS, and the Buk-M3 in PVO-SV, this will become even more of a problem. Naturally the earth’s curvature dramatically affects radar range against a low flying target, but there is a great deal of complexity that goes into assessing a radar’s effective targeting range over the horizon – especially since atmospheric conditions and terrain play an important role. I’m an expert on none of these things, but Russian search and fire control radars frequently come mounted on 24 or 40 meter masts. We should ask why.

Some basic calculators I found online show that all things being equal against a target flying at 100 meters your targeting range from a 5 meter height is only 27km, but from a 24 meter height you get 62km and from a 40 meter height 67km (hopefully I got those right). I’m not a radar expert, but the Russian military likes to put them on telescopic masts for a reason. If you can see the air defense radar in a 4th gen aircraft then it can probably see you. This problem might be solvable by pop-up attacks when dealing with semi-active radar missiles, but then you have a batch of 9M96 active seeking missiles to deal with because the radar only needs to see you for a brief amount of time and the missile seeker will figure out the rest of the problem.
It is also worth mentioning that the proliferation of Russian over the horizon radar systems pose a challenge for launching an aerospace attack undetected at any altitude. The relatively short range Podsolnukh-E, which uses the ocean as a conducting surface can see 450km out and being deployed with every Russian fleet. Strategic OTH systems like Container are located deep inside Russia and can see most of Europe’s airspace at ~3000km range. This simply means that Russian VKS will see an aerospace attack coming whether it is high, medium, or low altitude and without that element of surprise you get more attrition.
The last problem is that by avoiding VKS IADS an aircraft may quickly become best friends with Russia’s PVO-SV.
The PVO-SV problem for low or medium altitude
Air defense units belonging to the Russian land forces (PVO-SV) do not need VKS IADS, because they carry a thicket of their own air defense systems to cover the maneuver formations. These include Tor-M1, Buk-M2, various radar assisted gun systems, and MANPADS. The problem with attempting low altitude penetration or close air support against Russian ground forces is that they have a very high density of short range air defense systems able to reach to medium altitude.
Newer systems add to the challenge. Buk-M3 is much more capable than its predecessors, with active radar homing missiles (70km on 9R31M), a separate radar that can be raised on a retractable mast, and a containerized missile for quick reloads. These more capable systems are to be found in air defense brigades include S-300V4 and Buk-M3, while M2 is probably going to stick around in air defense regiments/brigade. Almost anything in the PVO-SV arsenal can shoot down cruise missiles, although that’s not their primary mission.

Meanwhile S-300V4 is really the mobile missile defense system for the Russian ground forces, designed to provide standoff capability against high value aerial assets like AWACS, or jammer aircraft. In terms of capability this has always been a more interesting system than the S-400, because of its ability to engage ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and maneuverable aerodynamic targets. This system was deployed to Syria, and largely unnoticed given the fixation on the S-400. Antey fielded a 400km missile against low maneuverability targets, 9M82 ‘Giant’, well before the 40N6 went into development for the S-400. The 9M83 ‘Gladiator’ missile is comparable to the 48N6 line, and the system components are tracked which makes them quite mobile. S-300V4s are due for an upgrade, and will be bought in increasing numbers for Russian air defense units assigned to fleets. I would watch this space – PVO-SV is going to get a lot more capable in the coming years.

Wrapping up
So Russian A2/AD is overrated in large part because of our own technology fetishism and terrible understanding of how Russian forces are actually organized. It does not exist as a doctrine, or a military strategy, but we should not over simplify the discussion in attempts to debunk the tactical capabilities of Russian military technology. All you have to do to achieve air dominance is eliminate the VKS radars, the low-frequency radars, and the Russian air force – then you’re largely ok right after dealing with the countless PVO-SV air defense systems. Assuming you don’t run out of munitions early on into this process, or aircraft, and all the high value enabling platforms do not get attrited, then it’s a manageable problem.
In some respects Russian IADS are a sort of McGuffin plot vehicle. As long as time and munitions are spent on them, Russian critical objects are safe, and one way or another the IADS end up executing their mission – which is not to defend themselves but to defend that which is strategically significant for the success of operations in the TVD.
In my view the balance of aerospace assault vs air defense remains offense dominant (I understand offense/defense dominance is not a thing because Keir Lieber says so), but that is probably not enough to offer confidence in the initial period of war. The problem is that Russia’s military has always seen defense to be cost prohibitive, and there for focused on an offensive damage limitation strategy + functional defeat of the adversary. So whether you think Russian A2/AD systems are amazing, or overrated, just remember – there is no such doctrine or term in the Russian military and the conversation misses the plot on how Russian forces actually organize at the operational-strategic level.
For a better, but longer explanation on operational level organization in the TVD, and Russia mil strategy check here.




Michael, another great article. It’s great to clearify that apparently aggressive Russian focus on strike capability is basically an affordable deterrent. I’ll repost it on Twitter if you don’t mind.
Another question: do you have any source or personal views on Russian contemporary submarine strategy? The topic is heating up after the largest post-1991 sub drills last November and introduction of new platforms like Yasen-M. I believe analytics overlooked how revolutionary it is. I understand how sensitive sub tech is and I see the lack of information, but introduction of natural circulation cooling reactor with no circulation pumps (i.e. main noise source on nuclear sub) is pretty big deal as per globalsecurity.com, Paralay etc. So I would really appreciate your view on what are they trying to achieve and how and what’s new from the old naval bastion concept.
LikeLike
I do have views on Russian naval strategy that I hope to write up. Have not touched on the topic since some Proceedings series articles in 2017 I think, that were also posted to this blog if you search the archive. I would summarize those views as:
1. the bastion or protected maritime region concept remains, but makes little sense given the small size of Russia’s Navy and the much larger size of the road mobile ICBM force. They’re spending a great deal on Borei SSBN + Bulava program, and Delta IV extension.
2. the rest of the Navy has a damage limitation (not A2/AD) job, to attrition U.S. naval forces at 2000+ km range – this strategy endures since about 1964. Probably sea control in near sea zone and sea denial in far sea zone is the way I would put it.
3. Post-2010 Russian Navy has picked up an important role in strategic operations, functional designation as strategic deterrent forces with long range cruise missiles and non-strategic nuclear. Basically escalation management, strategic operations dealing with critical infrastructure. I think once Tsirkon comes online it will make that mission set even more viable.
4. Yasen 885M – If there’s one 4th gen submarine that seems quite capable, and has a land attack strike package of conventional or nuclear tipped cruise missiles, then that’s probably the Yasen class.
LikeLike
If we assume full replacement of Topol and Topol-M TELs with Yars series TELs we would see ~180 TELs (based on FAS-2019 report), if we assume a 10 strong Borei program we would see ~160 Bulava SLBM launchers. While the throw weight of the two is broadly (in NST terms) compatible Bulava is cited to carry more RVs. As such it is hard to say if the TEL based ICBM force is “much larger”. At present this is reinforced due to R29 mods having better throw weight of Bulava, use of monoblock Topol, Topol-M.
Then we are going into the discussion of readiness of said launchers but both TELs and SSBNs appear to have low readiness so I would be careful about attributing higher readiness to either and as such I am uncertain if relative readiness could be used as an argument for “much larger”.
LikeLike
Let me come back to this. When I wrote much larger I meant relative to what it was as a share of the overall strategic nuclear force – not larger than the number of warheads deployed on SSBNs. That’s not at all clear from what I wrote because I wrote that reply in a couple of minutes. I would not assume that road mobile RVSN forces have the same readiness as the ballistic missile submarine force, and they pose different problems in terms of what that readiness means – but this is pretty far off topic for the conversation in the original post.
LikeLike
@Anonymous:
The Russians have stated in their 2000 Naval Doctrine that they want 12 SSBNs. They’ve also had 12 until 2 were decommissioned in 2018. But new boats are coming, so it’s unlikely that current all time low of 10 subs would be maintained plus the US still operates 14. Note that in 2010 they decommissioned two SSBNs at Pacific fleet and they were replaced only in 2014. So delays and small variations in numbers are normal.
LikeLike
Michael, yes, for example if we take START-I as basis then TEL ICBM launchers formed what, 12 percent of the overall force? So in this sense I guess you are right, there was a shift towards a greater share of ICBM TELs when compared to the legacy era.
Svit, I am aware of this, I was just being conservative in presenting my argument.
LikeLike
Thank you for the article, Michael. Helped me understand the S-350’s role as a replacement for the earlier S-300s. However, why didn’t they just deploy more short range S-400 variants to replace those older S-300s? Not sure I see the value of yet another system in their already zoo-like park of vehicles/platforms.
“Reading Russian military thought articles on the problem of U.S. massed aerospace assault, and the damage that numerous long range precision guided munitions could inflict, one gets the impression that they understand where things stand perfectly well – and they don’t like it.” Can you provide a few links to read more about this?
LikeLike
There are links in the WOTR article. S-400 was initially meant to have a quad pack canister to launch smaller active radar missiles, but they changed this to S-350 which can take over for S-300P+ variants. The S-400 is still sighted with that small quad canister pack in multinational events – so it didn’t necessarily just go away. The value of S-350 is to deal with saturation and handle the mid-range defense at 100-120km which was the S-300 job. I think the idea being that its going to be cheaper and less of a strategic system.
LikeLike
Many things still can (will?) change with aircraft self-defense missile introduction (e. g . Cuda). Russian long range missiles are pretty big, visible and vulnerable (due to speed) targets themselves and also (theoretically) can be intercepted by similar own ground systems (like Israeli Arrow “downing” Syrian S-200) over the “theater”. “David’s Sling” seems to be able to do it. Also still actually there is no any remedy from saturation using smart decoys (TALD, MALD and creatures like future Gremlins) for long range systems.
As for antenna masts mentioned – according to Pythagoras 100 m target altitude gifts us 35700 m to horizon, 24 m – 17487 m, 40 m – 22576 m, so detection ranges with raised antennas will be slightly smaller – 43187 and 48276 m.
LikeLike
I won’t comment on all the missile mumbo jumbo except to say that the fans are always wrong, and this is best to forum enthusiasts to debate with each other which toy does what best. Much is contingent, and a lot of tactical stuff doesn’t add to what you want to get out of it in aggregate. As the article states – it will either go really well, or really poorly, and the country with the best hedge strategy + ability to adapt will do the best.
Here is a radar horizon calculator, it gets the numbers it gets: http://www.mar-it.de/Radar/Horcalc/horcalc.htm the others I have seen produce the same numbers. You can build your own online, I’m sure many will use it.
LikeLike
Basic exposition of the role and limitations of the Russian Navy is contained in the UNCLASSIFIED publication “THE RUSSIAN NAVY – A Historic Transition” issued by the Office of Naval Intelligence in December 2015. It can be found at http://www.ONI.NAVY.MIL
LikeLike
I think George’s work gets it about right in that ONI piece, although I prefer damage limitation to layered defense as the descriptor, this is a narcissism of small differences.
LikeLike
Layered defense as opposed to elastic defense.
LikeLike
I used “layered defense” because that is the way the Russians view it regarding the threat from US/NATO. Given the extent of the Russian forces and their capabilities, their approach is to have sufficient force (defensive sufficiency) to deter an attack.
By the way, the 28 Jan post by “George” was not mine.
LikeLike
So I think it is fair to say that layered defense is the Russian perspective, but what the strategy means in practice for us is damage limitation. The screw turns on the question of whether Russian forces must eliminate the threat left of launch, or can just sit there and ‘defend.’ Because actual defense against sizable cruise missile strikes is not viable, implementation results in a damage limitation approach to have any viability. There’s a secondary functional split between the navy’s role as a general purpose force ( and its role as part of strategic deterrence forces (СОН vs ССС)
LikeLike
A very interesting article Mr. Kofman
If you don’t mind however I would like to ask a question related to the topic, you talked about the various missile systems, fighters and radars posses by the Russian Military and their role as part of Russia’s Air Defense and how they are likely to be used in the event of a conflict., There are three combat systems however that were not mentioned and I would like to hear your opinion as to their potential role as part of Russia’s IADS and what they add if anything to the picture in terms of air defense.
The systems in question are Drones, Electronic Warfare Systems and Direct Energy Weapons like the Peresvet that Putin showed in March 2018.
LikeLike
I don’t see drones as part of this picture yet, except for Okhotnik. Need to see more of that drone to understand what role it will play in VKS and its role.
EW plays a big role in supporting air defense, and in identifying targets. How effective it will ultimately prove is hard to tell. A lot of current claims about EW are inflated, but I think the really interesting systems have only recently entered the Russian military’s repertoire. The directed energy weapons so far seem to be counter space dazzling systems from what I can tell of Peresvet, the other systems seem to be point defense against missiles. RF VKS helicopters in Syria carry those packages.
LikeLike
Altius appears to be an ISR/patrol drone which would be a valuable asset considering the problems raised in your follow up article.
LikeLike
Good points, well made.
One aspect of low altitude penetration that you have not mentioned (and which militates against its effectiveness as a response) is that terrain masking works both ways. Not only does it cut the detection range of air defences, it just as severely affects the range of the aircraft’s own sensors.
Low release altitude also impacts the range of both the launch platform and its weapons. While modern networking with SatCom and data-link for off-board targeting may mitigate the detection range problem somewhat, these problems won’t go away so easily. Weapons range is a particularly serious one for Western air forces that rely heavily on low-cost free-fall PGMs which only have any practical stand-off capability if dropped from 30000ft or more. Excepting expensive, very large ALCMs like JASSM and StormShadow, there are virtually no powered AGMs for mobile targets of opportunity left in Western arsenals. Until the advent of AARGM-ER & SiAW, free-fall weapons were even expected to take on the DEAD role which is only credible if stealth works as advertised (altitude for SAR or EO targeting and stand-off range). But if it doesn’t, a SDB dropped from 200ft will be reduced to single-digit kilometers in range, rather than 100km at altitude. As for the launch platform, a typical tactical combat aircraft might lose 60% of its high-altitude combat radius if required to fly the entire mission on the deck. As a result, the target set which can be threatened is severely constrained, or use of scarce tanker assets dramatically increased.
There are multiple very good reasons why low altitude penetration is deprecated. If Russian air defences succeed in forcing an aerospace attack down into the weeds they will have already blunted its spear considerably just by virtue of doing this.
LikeLike
This is quite right. I did not want to get into the weeds of the problem set which could form an entire separate article, and does not play to my strengths. Some aspects of air power are much better left to those with experience and knowledge of the nuances. There is a series of articles on low altitude penetration that can be found on WOTR with some good discussions related to this subject. Much of what has been alleged about the potential benefits of low altitude penetration was done by analysts who sort of imagine that its just a thing one can do, without addressing the realities you mention above.
I wanted to add to this conversation the part where some of the benefits of low altitude penetration are lost at the operational level if you are dealing with strategic OTH-B radars and a common operating picture for enemy air defense forces, because it eliminates the benefit of surprise.
LikeLike
I have found this site and know you all are experts in yours areas. I am an old retired Air Force Imagery Analyst with nothing else to do but exploit the unclassified imagery available on line. While not real time, I can conduct some 3rd phase exploitation. I have noticed deployment of a Domed system that resembles the old Softball system going into the sites along the Baltic and Finnish Borders, the Black Sea coast and the Caucuses. The collocate with the EW sites and started around 2016. I can’t find any information on this equipment. Do you have any knowledge on this or is this in classified channels. It is interesting to see the upgrades that took place 2010 to 2016 and continuing today. Thanx
LikeLike
Dear anonymous,
If you do not share a picture or location of “this site” you found, do not expect that anyone will be in a position to discuss it with you.
LikeLike
460359N0381137E, 445025N0372110E, 673605N0302928E, 665833N0302245E, and 20 other locations. Collocated with EW sites. Seems between 2014 and 2016 in the Joint Arctic and Western MD and 2016 and 2018 in the Southern MD. They also have 4 at the SAM Brigades around the Moscow Ring. Thanks For Replying
LikeLike